题型:任务型阅读 题类:真题 难易度:困难
2012年高考英语真题试卷(湖南卷)
Directions: Read the following passage. Fill in the numbered blanks by using the information from the passage.
Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer.
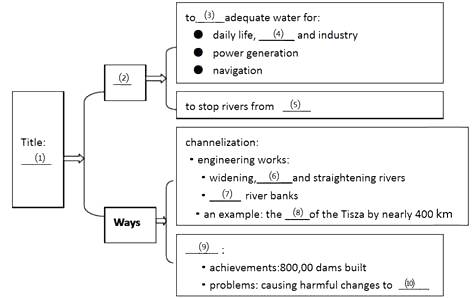
Since the earliest civilizations, people have controlled rivers to meet society's demands. Today, rivers are controlled for many reasons, primarily to maintain reliable water supplies for daily, agricultural and industrial needs, for power generation, for navigation (航行), and to prevent flooding.
River control is achieved by channelization, a term that covers a range of river engineering works, including widening, deepening, straightening and stabilization of banks, and by the construction of dams.
An important period of channelization took place in Europe during the l9'th century, when many large rivers were straightened and their beds deepened. One of the most dramatically changed was the Tisza River, a branch of the Danube that flows through Hungary. The controlling of the Tisza, designed to reduce flooding and make land for agriculture, included cutting off more than 100 meanders (河曲), shortening the river's length by nearly 400 kilometers.
One of the most common ways in which people control rivers is by damming them. The past 50 years or so has seen an increase in dam construction worldwide, and at the beginning of the 21st century, there were about 800,000 dams globally, some towering more than 200 meters in height.
Despite their successes, many dams also cause significant environmental changes that prove harmful. Some particularly deep reservoirs (水库) can bring about earthquakes due to the stress on their bottom rocks caused by huge volumes of water. Downstream of a reservoir, the river is certainly influenced in many ways: water volume, speed and quality are all affected, leading to changes in the landscape and among plants and animals.
⑴ ⑵ ⑶ ⑷ ⑸ ⑹ ⑺ ⑻ ⑼ ⑽
If you can find a tree which has been cut down,you will see many rings,or circles,on the base of the trunk.By learning to read these rings,you can find out about the tree's life.
The number of rings tells you how old the tree is.Each year,new wood is formed on the outside of the tree.This new wood is light in color when the tree is growing in spring and summer,and dark in winter when the tree is not growing much.So,if you count the rings of darkorlight colored wood,you can often find out how old the tree is.
You can also tell which years have been good years and which years have been bad years.When the lightcolored rings are very wide,it means that the tree has been growing quickly that year.If the rings are narrow,it has been growing slowly.If the rings on a tree trunk were greatly magnified,you would be able to see why the rings are lightcolored when the tree is growing quickly and darkcolored when the tree is growing slowly.The tree trunk is made up of microscopic tubes,like some pipes,carrying water from the soil,through the trunk,and up to the leaves.They are wide and thinwalled when the tree is growing quickly and they are carrying a lot of water.They are narrow and stuck together when the tree is not growing so quickly.
When a tree is old,the tubes in the centre of the tree don't carry water.The walls of the tubes have become thick with materials which have stuck along them over the years,forming a kind of wood called“heartwood”.This kind of wood is darker in color than the young,growing wood on the outside of the tree.
You don't very often see whole tree trunks which have been cut across.But once you learn to read a cross section of the wood,you can see much more in wood which has been used to make boxes,houses and other things.
In most wood,instead of seeing the trunk cut across,you are seeing it cut along its length.Because you don't see the whole tree,you can't tell how old it is.
Title:{#blank#}1{#/blank#} of a Tree
General information | Old trees | ||
Items | Facts | Items | Facts |
Where can rings be seen | On the {#blank#}2{#/blank#} of a trunk | The tubes in the centre of the tree | Don't carry water |
The{#blank#}3{#/blank#} of rings | Helps us know about its age | The walls of the tubes | Become {#blank#}4{#/blank#}; Form {#blank#}5{#/blank#} |
{#blank#}6{#/blank#} lightcolored rings | Show the tree grows quickly | ||
Narrow{#blank#}7{#/blank#} rings | Mean the tree grows slowly | ||
Microscopic tubes | Function | Carry{#blank#}8{#/blank#} | |
Features | Wide and {#blank#}9{#/blank#} when growing quickly | ||
Narrow and stuck together when growing {#blank#}10{#/blank#} | |||
Brainstorming for Ideas
Try blind writing. When trying to get past a writing block or a brainstorming lag, take at least ten minutes to sit down and write. Force yourself to write for the full ten minutes, no matter what comes of it. The act of putting pen to paper will stimulate the part of your mind that generates ideas.
Make a mind map. Mind mapping is a brainstorming strategy that allows you to map out different tangents of thought to stimulate new ideas. Get a piece of paper, poster board, or whiteboard and write your goal in the center. Write subtopics and related thoughts around the goal, and continue branching out from them to develop your train of thought. For example, a mind map about the environmental goal “Going Green” could branch into subtopics such as “Reducing Waste”, “Eco-travel”, and “Global Warming”.
Attempt “rolestorming”. For a fresh perspective on a topic,attempt “rolestorming”. Picture yourself as someone else (e.g. a parent, friend, colleague, or partner) and imagine how you would approach a scenario as them. You can extend this brainstorming technique to famous people or historical figures (e.g. Albert Einstein, Bill Gates).
Try meditation. To open your mind to new ideas, try meditation. Find a peaceful place to sit quietly and focus on the question at hand (e.g. “How can I promote my new business on my limited budget?”). Bring a pen and paper to jot down ideas, and meditate for about 30 minutes, or until a good idea comes to you. To avoid worrying about the time, set an alarm on your phone to signal the 30 minute mark.
Remove limitations. Remove the limitations that may be hindering your brainstorming progress by approaching the subject as if there were no obstacles. While this process may not yield feasible solutions right away, it will open your mind to possibilities you would not look at otherwise. For instance, when planning a surprise party, you might overlook certain venues because of financial constraints, such as an expensive French restaurant that your friend would love to try. By allowing your mind to go there during brainstorming, you might get the idea to simulate the restaurant and meal for a house party.
Discuss things in a group. Group brainstorming sessions can allow you to develop your thoughts by feeding off of the ideas of others. If you are working on a group project or collaboration, schedule brainstorming time in a quiet location with no disturbance. If you are working on your own project, ask friends or colleagues if you can bounce ideas off of them and get their input.
Brainstorming for Ideas | |
Passage outline | Supporting details |
Try blind writing. | •Force yourself to write for the full ten minutes,{#blank#}1{#/blank#} comes of it. •The part of your mind that generates ideas will be {#blank#}2{#/blank#} by the act of putting pen to paper. |
Make a mind map. | •Mind mapping is a brainstorming strategy allowing you to find out different ways to stimulate new ideas. • Get a piece of paper, poster board, or whiteboard and write your {#blank#}3{#/blank#} in the center. • Branch out from subtopics and related thoughts to {#blank#}4{#/blank#} your train of thought. |
{#blank#}5{#/blank#} “rolestorming”. | •Picture yourself as someone else and imagine how you would approach a scenario as them. • This brainstorming technique can be {#blank#}6{#/blank#} to famous people or historical figures. |
Try meditation. | •Find a peaceful place to sit quietly and focus on the question at hand. •Bring a pen and paper to jot down ideas, and meditate for about 30 minutes, or until you {#blank#}7{#/blank#} up with a good idea. |
Remove limitations. | • {#blank#}8{#/blank#} the limitations that may be hindering your brainstorming progress by approaching the subject as if there were no obstacles. • While this process may not bring out practical solutions {#blank#}9{#/blank#}, it will open your mind to other possibilities. |
Discuss things in a group. | • When cooperating with others, remember to brainstorm quietly without being {#blank#}10{#/blank#}. |
试题篮