阅读理解
British children used to play conkers (板栗游戏) in the autumn when the horse-chestnut
trees started to drop their shiny brown nuts. They would select a suitable
chestnut, drill a hole in it and thread it onto a string, then swing their
conker at that of an opponent until one of them broke. But the game has fallen
out of favour. Children spend less time outdoors and rarely have access to
chestnut trees. Besides, many schools have banned conkers games, worried that
they might cause injuries or nut allergies.
That sort of risk-averseness(规避风险) now spreads through every aspect of
childhood. Playgrounds have all the excitement designed out of them to make
them safe. Many governments, particularly in societies such as America, have
tightened up their rules, requiring parents to supervise(监管) young children far more closely than
in the past. Frank Furedi of the University of Kent, a critic on modern
parenting, argues that allowing children to play unsupervised or leaving them
at home alone is increasingly described as a symptom of irresponsible
parenting.
In part, such increased caution is a
response to the huge wave of changes. Large-scale urbanization, smaller and
more mobile families, the move of women into the labor market and the
digitization of many aspects of life have unavoidably changed the way that
people bring up their children. There is little chance that any of these trends
will be changed, so today's more intensive(精细化 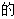 ) parenting style is likely to go on.
) parenting style is likely to go on.
Such parenting practices now embraced by wealthy parents in many parts of the rich world, particularly in America, go far beyond an adjustment to changes in external conditions. They mean a strong bid to ensure that the advantages enjoyed by the parents' generation are passed on to their children. Since success in life now turns mainly on education, such parents will do their best to provide their children with the schooling, the character training and the social skills that will secure access to the best universities and later the most attractive jobs.
To some extent that has always been the case. But there are more such parents now, and they are competing with each other for what economists call positional goods. This competition starts even before the children are born. The wealthy classes will take their time to select a suitable spouse and get married, and will start a family only when they feel ready for it.
Children from less advantaged backgrounds, by contrast, often appear before their parents are ready for them. In America 60% of births to single women under 30 are unplanned, and over 40% of children are born outside marriage. The result, certainly in America, has been to widen already massive social inequalities yet further.
All the evidence suggests that children from poorer backgrounds are at a disadvantage almost as soon as they are born. By the age of five or six they are far less "school-ready" than their better-off peers, so any attempts to help them catch up have to start long before they get to school. America has had some success with various schemes involving regular home visits by nurses or social workers to low-income families with new babies. It also has long experience with programmes for young children from poor families that combine support for parents with good-quality child care. Such programmes do seem to make a difference. Without extra effort, children from low-income families in most countries are much less likely than their better-off peers to attend preschool education, even though they are more likely to benefit from it. And data from the OECD's PISA programme suggest that children need at least two years of preschool education to perform at their best when they are 15.
So the most promising way to ensure greater equality may be to make early-years education and care for more widely available and more affordable, as it is in the Nordics. Some governments are already rethinking their educational priorities, shifting some of their spending to the early years.
Most rich countries decided more than a century ago that free, compulsory education for all children was a worthwhile investment for society. There is now an argument for starting preschool education earlier, as some countries have already done. In the face of crushing new inequalities, a modern version of that approach is worth trying.